Resources
CICERO : A Dataset for Contextualized Commonsense Inference in Dialogues
We introduced
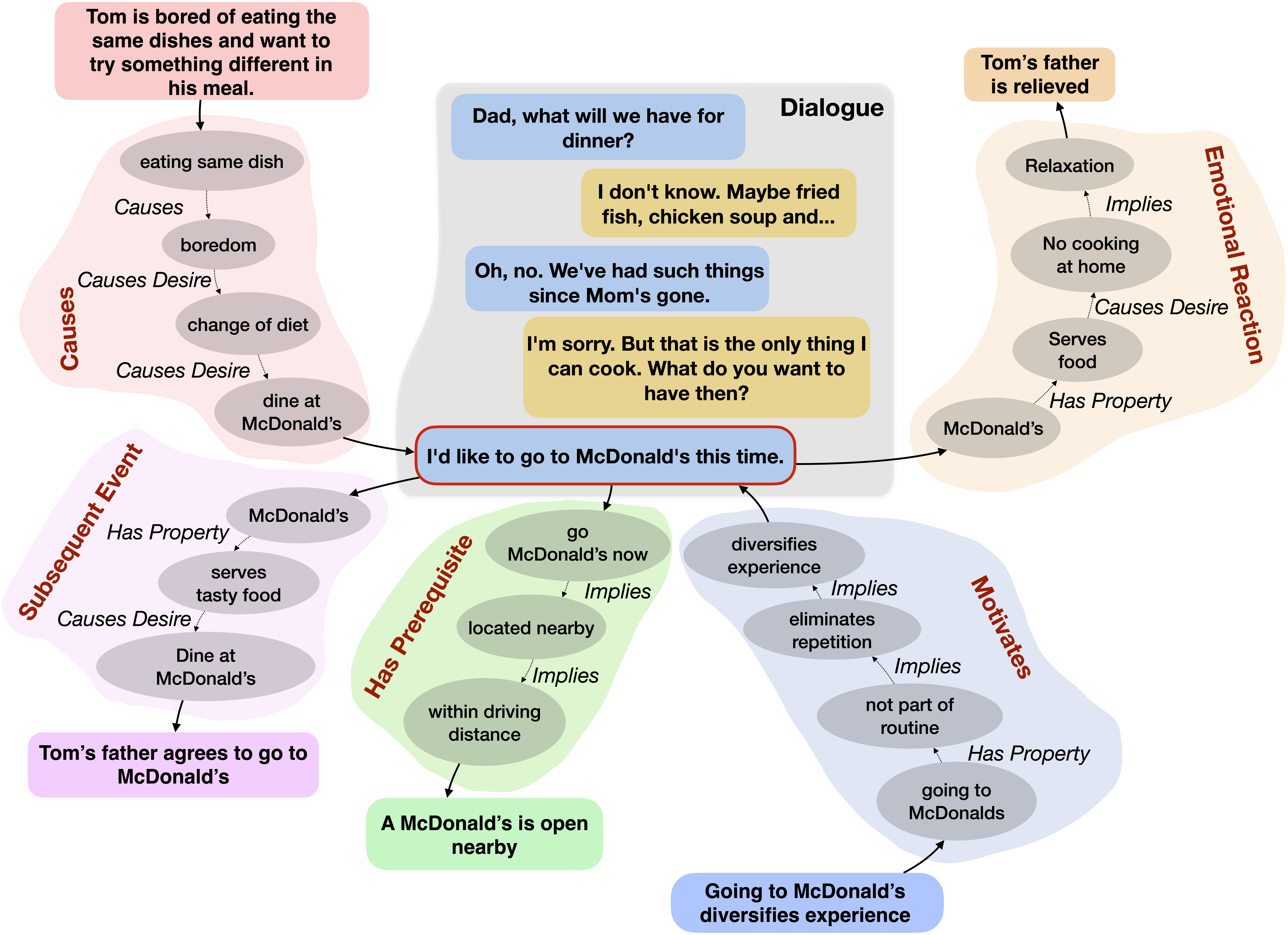
CIDER: Commonsense Inference for Dialogue Explanation and Reasoning
Commonsense inference to understand and explain human language is a fundamental research problem in natural language processing. Explaining human conversations poses a great challenge as it requires contextual understanding, planning, inference, and several aspects of reasoning including causal, temporal, and commonsense reasoning. In this work, we introduce CIDER – a manually curated dataset that contains dyadic dialogue explanations in the form of implicit and explicit knowledge triplets inferred using contextual commonsense inference. Extracting such rich explanations from conversations can be conducive to improving several downstream applications. The annotated triplets are categorized by the type of commonsense knowledge present (e.g., causal, conditional, temporal). We set up three different tasks conditioned on the annotated dataset: Dialogue-level Natural Language Inference, Span Extraction, and Multi-choice Span Selection. Baseline results obtained with transformer-based models reveal that the tasks are difficult, paving the way for promising future research.
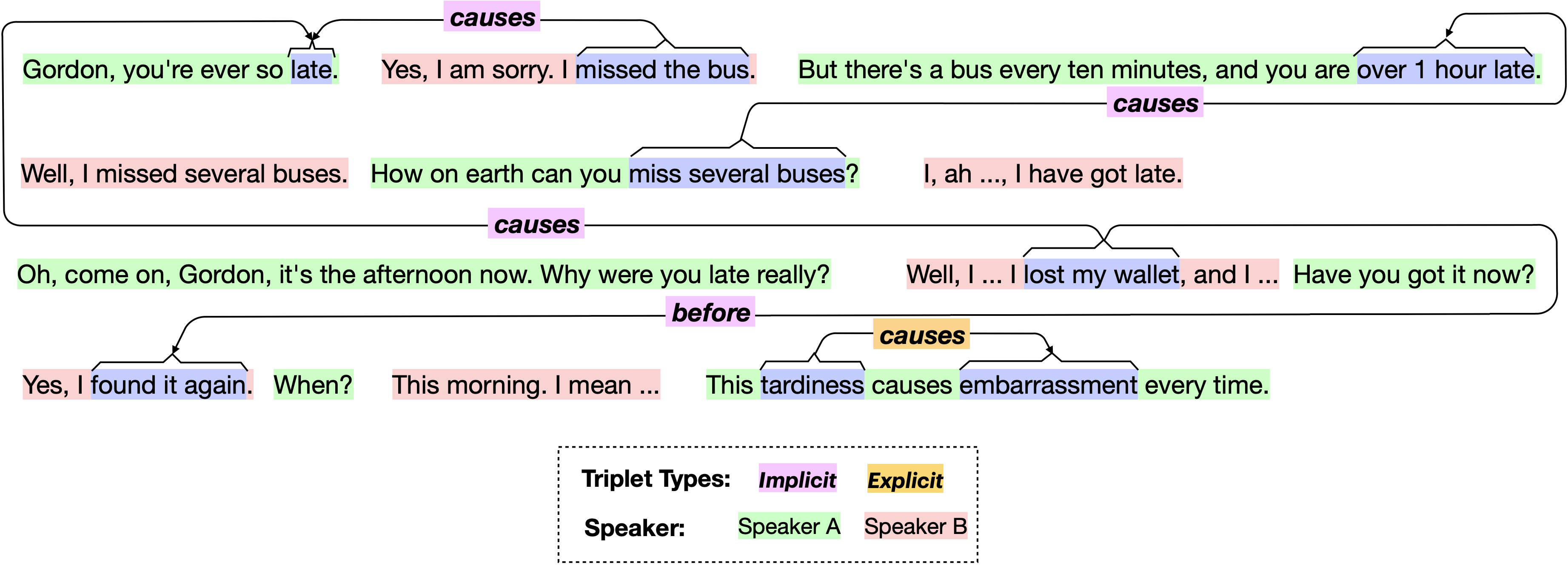
RECCON: Recognizing Emotion Cause in Conversations

Recognizing the cause behind emotions in text is a fundamental yet under-explored area of research in NLP. Advances in this area hold the potential to improve interpretability and performance in affect-based models. Identifying emotion causes at the utterance level in conversations is particularly challenging due to the intermingling dynamic among the interlocutors. To this end, we introduce the task of recognizing emotion cause in conversations with an accompanying dataset named RECCON. Furthermore, we define different cause types based on the source of the causes and establish strong transformer-based baselines to address two different sub-tasks of RECCON: 1) Causal Span Extraction and 2) Causal Emotion Entailment.
MUStARD: Multimodal Sarcasm Detection Dataset

We release the MUStARD dataset which is a multimodal video corpus for research in automated sarcasm discovery. The dataset is compiled from popular TV shows including Friends, The Golden Girls, The Big Bang Theory, and Sarcasmaholics Anonymous. MUStARD consists of audiovisual utterances annotated with sarcasm labels. Each utterance is accompanied by its context, which provides additional information on the scenario where the utterance occurs.
MELD: A Multimodal Multi-Party Dataset for Emotion Recognition in Conversations
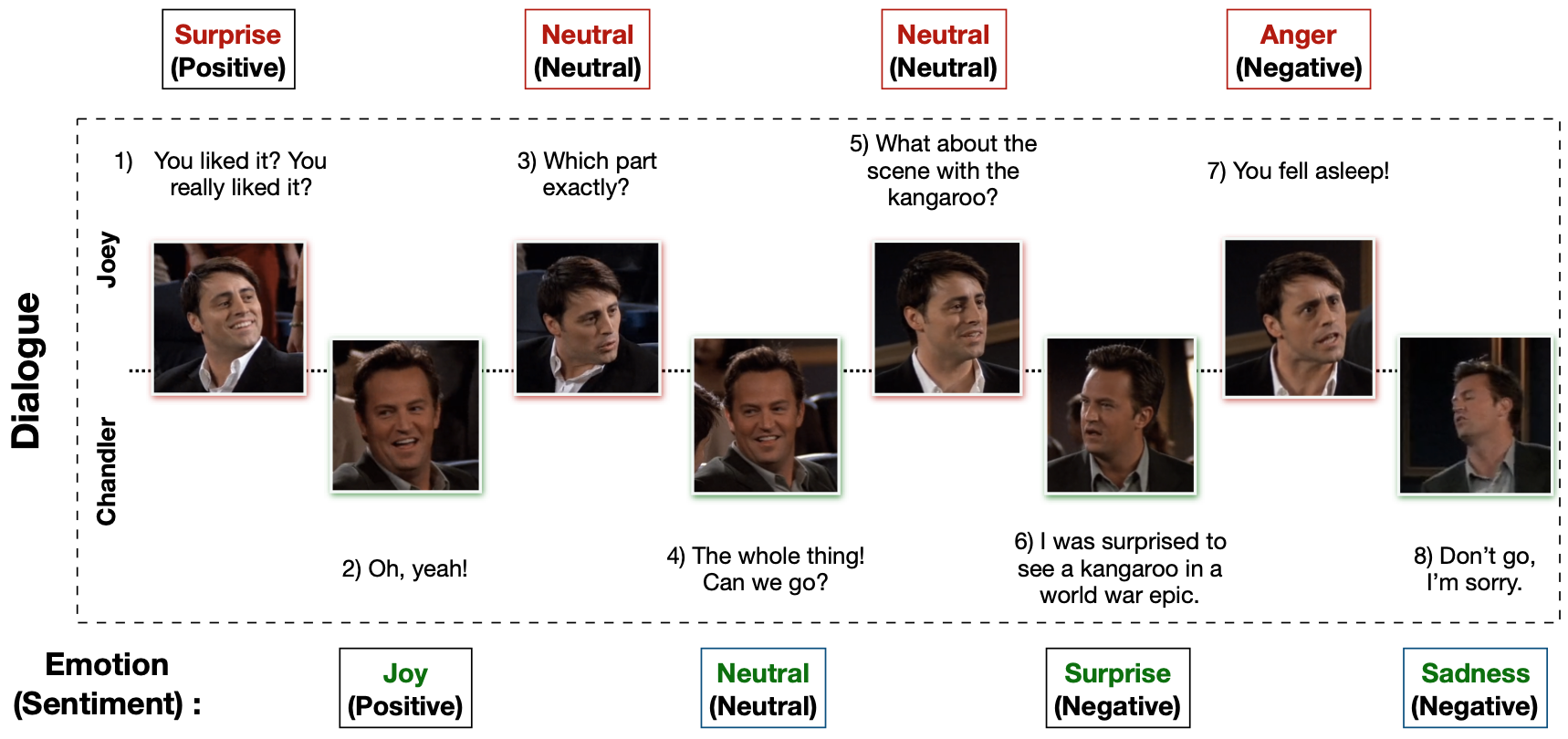
Multimodal EmotionLines Dataset (MELD) has been created by enhancing and extending the EmotionLines dataset. MELD contains the same dialogue instances available in EmotionLines, but it also encompasses audio and visual modality along with text. MELD has more than 1400 dialogues and 13000 utterances from Friends TV series. Multiple speakers participated in the dialogues. Each utterance in a dialogue has been labeled by any of these seven emotions – Anger, Disgust, Sadness, Joy, Neutral, Surprise and Fear. MELD also has sentiment (positive, negative and neutral) annotation for each utterance.